Once a new software product has been produced it must be installed and then implemented on site.
There are a number of methods of introducing a new system and each of these methods suits different circumstances.
Usually installation will involve conversion from an old system that the new system is designed to replace, so often these methods are known as methods of conversion.
Students Learn About:
|
The implementation stage delivers the new information system to the participants.
- It involves using the solution to solve the problem.
- If a software package, such as database management system, is chosen, implementing a solution involves applying the software to the problem.
- The implementation phase may involve a major change in the way organisations operate.
- This requires conversion to the new system and training
Conversion
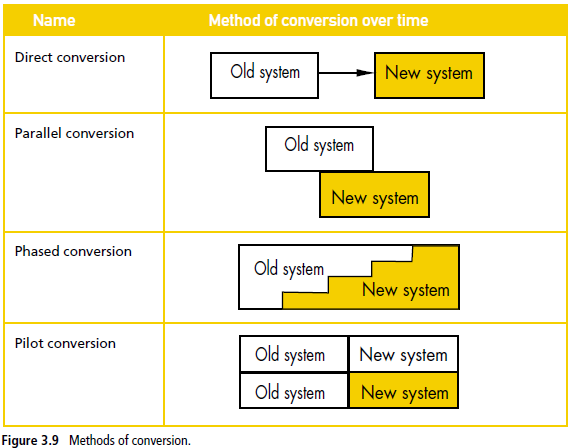
Conversion involves changing from the old system to the new system. It must be carefully planned and executed to avoid errors. The actual method chosen for conversion depends on the nature of the work and the characteristics of the new system. There are four methods of conversion: direct, parallel, phased and pilot.
Direct conversion involves an immediate change to the new system.
- A date is chosen on which the old system ends and the new system begins.
- All data from the old system is transferred to the new system.
- Direct conversion is not popular even though there are minimal transition costs.
- It does not allow time to check whether the new system will operate correctly and that participants understand the system.
- If the new system fails or problems occur, the old system is not available as a backup.
Parallel conversion involves the old and new systems working together for some time.
- Participants can compare the two systems and obtain a good understanding of the differences between them.
- If there are any problems with the new system they can be solved before the old system is discontinued.
- However, parallel conversion results in additional workloads for participants as they mustoperate both systems.
- It may also result in confusion about which system has the correct data.
Phased conversion involves the gradual implementation of the new system.
- Certain operations of the new system are implemented while the remaining operations are completed by the old system.
- When one operation of the new system is successful, another operation is implemented until the new system is Planning, design and implementation fully operational.
- Each operation is individually tested.
- If there is a problem with a certain operation it is possible to switch back to the old system.
- Unfortunately phased conversion is often confusing, with some participants working on the old system and some on the new system.
Pilot conversion involves trialing the new system in a small part of the organisation.
- The old system is still available if the new fails or experiences problems.
- Pilot conversion is usually undertaken by a keen group of participants who appreciate the benefits of the new system.
- If pilot implementation works, it is usually easier to motivate the other participants of the organisation to adopt the new system.
Implementation or Installation Methods - Easy way to remember
Useful Links:
Teach ICT Installation Methods 1
Teach ICT Installation Methods 2
Textbook Notes: